Managing Python Virtual Environments
Python environments can get complex and problematic without virtual environments. We can use venv module that comes built-in with Python to manage it, but it may get complex too after a while. For these needs specifically, virtualenvwrapper has been developed.
1. Install virtualenvwrapper
Install virtualenvwrapper with pip
sudo pip3 install virtualenvwrapper2. Find The virtualenvwrapper.sh
Virtualenvwrapper uses a sh file to initialize all the commands that we are going to use. In order to make it executable at the beginning of all sessions, we are going to add it to the .bashrc
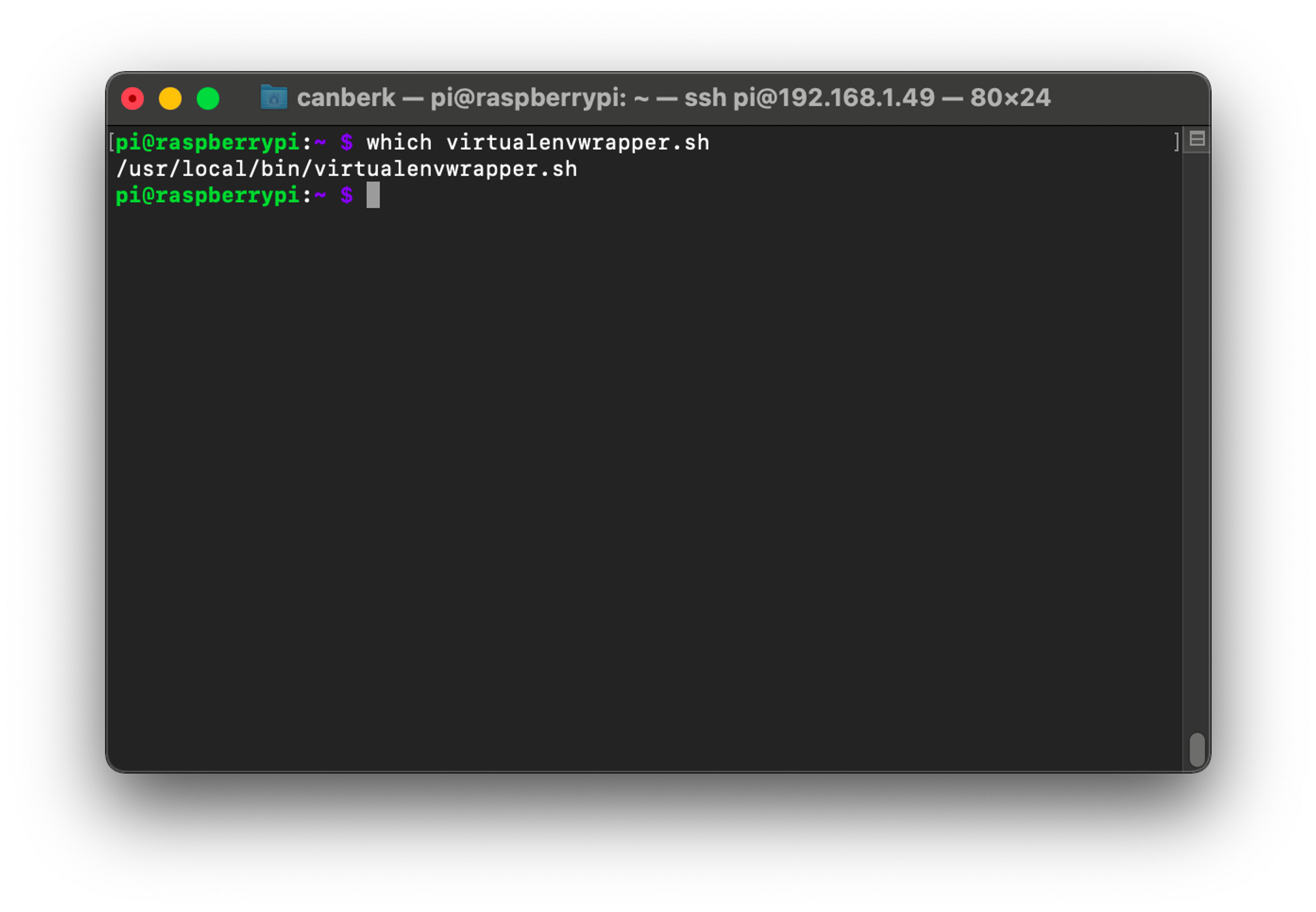
But first, we need to know where it is. To check the location of the virtualenvwrapper.sh, run the command below.
which virtualenvwrapper.shOutput on my system is as follows.
3. Add virtualenvwrapper.sh to the .bashrc
In order to add it to the .bashrc run the following commands, do not forget to replace the location if it is different.
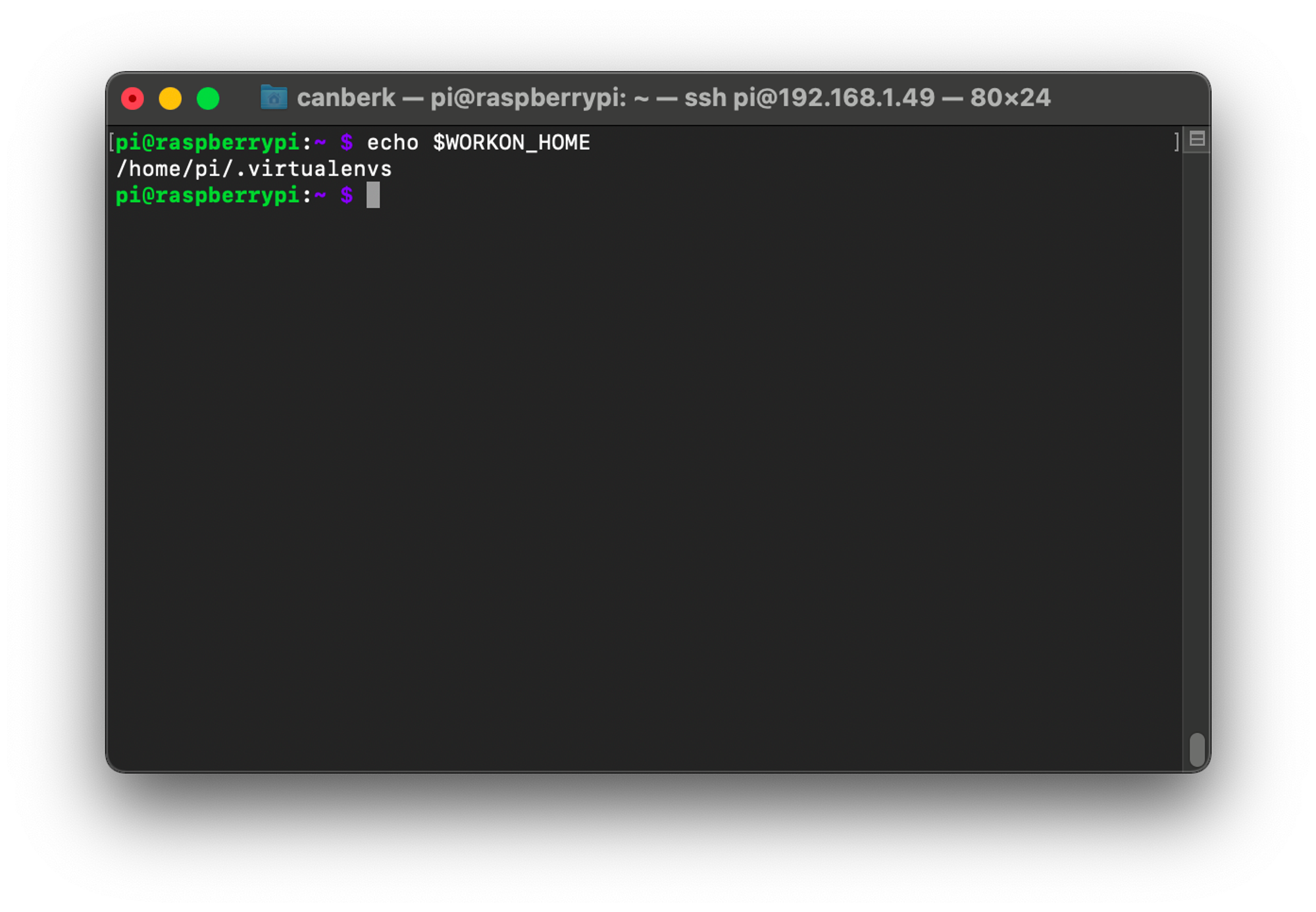
echo 'export VIRTUALENVWRAPPER_PYTHON=/usr/bin/python3' >>~/.bashrcecho 'export VIRTUALENVWRAPPER_VIRTUALENV=/usr/local/bin/virtualenv' >>~/.bashrcecho 'source /usr/local/bin/virtualenvwrapper.sh' >>~/.bashrcexec "$SHELL"echo $WORKON_HOMEWhen we execute echo $WORKON_HOME if we can get a location to a .virtualenvs directory, it means that our installation was successful.
4. Create a Virtual Environment
In order to create a virtual environment, you can use the mkvirtualenv command with a name of your choice for your new virtual environment.
mkvirtualenv testenv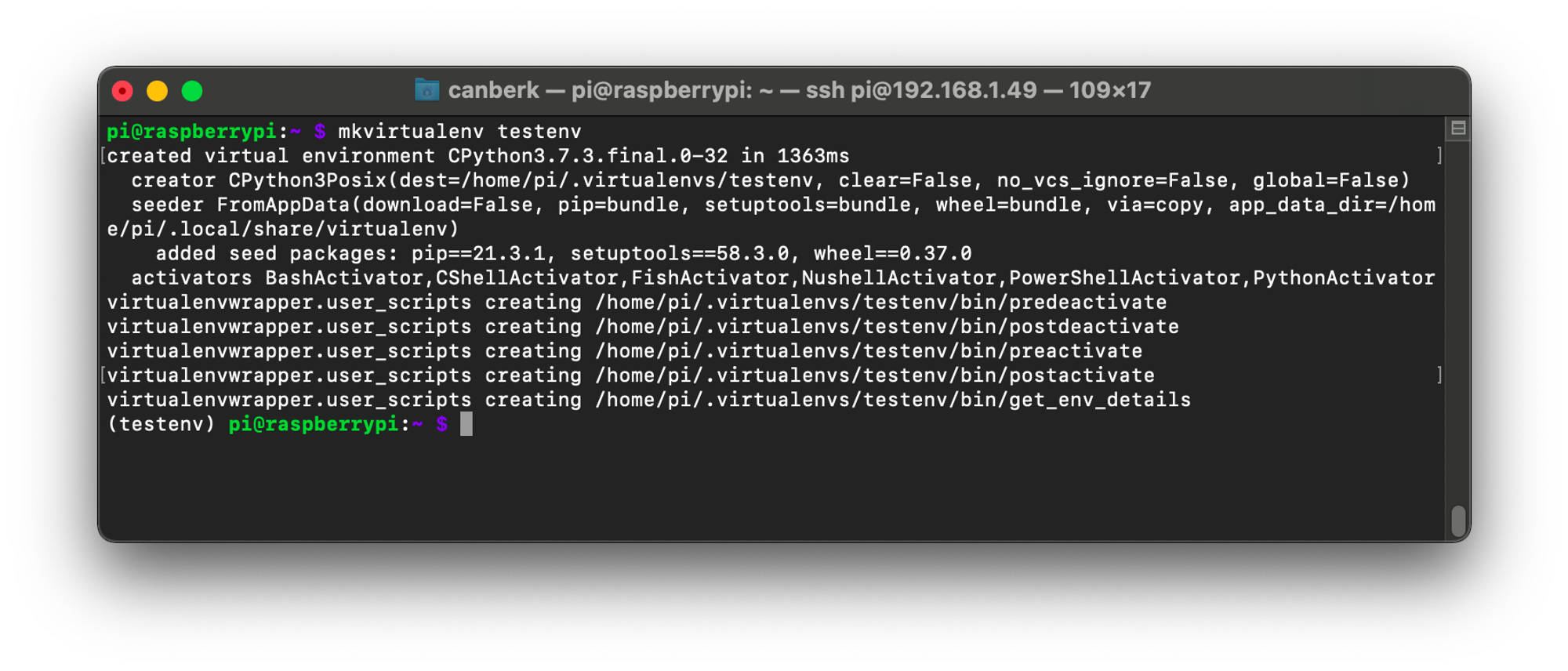
As can be seen above, a new virtual environment is created and activated. If we check the locations of Python and pip we can see that they are pointing to a different location than the system locations. Also, we can validate that we are working on a different environment by checking the installed pip packages.
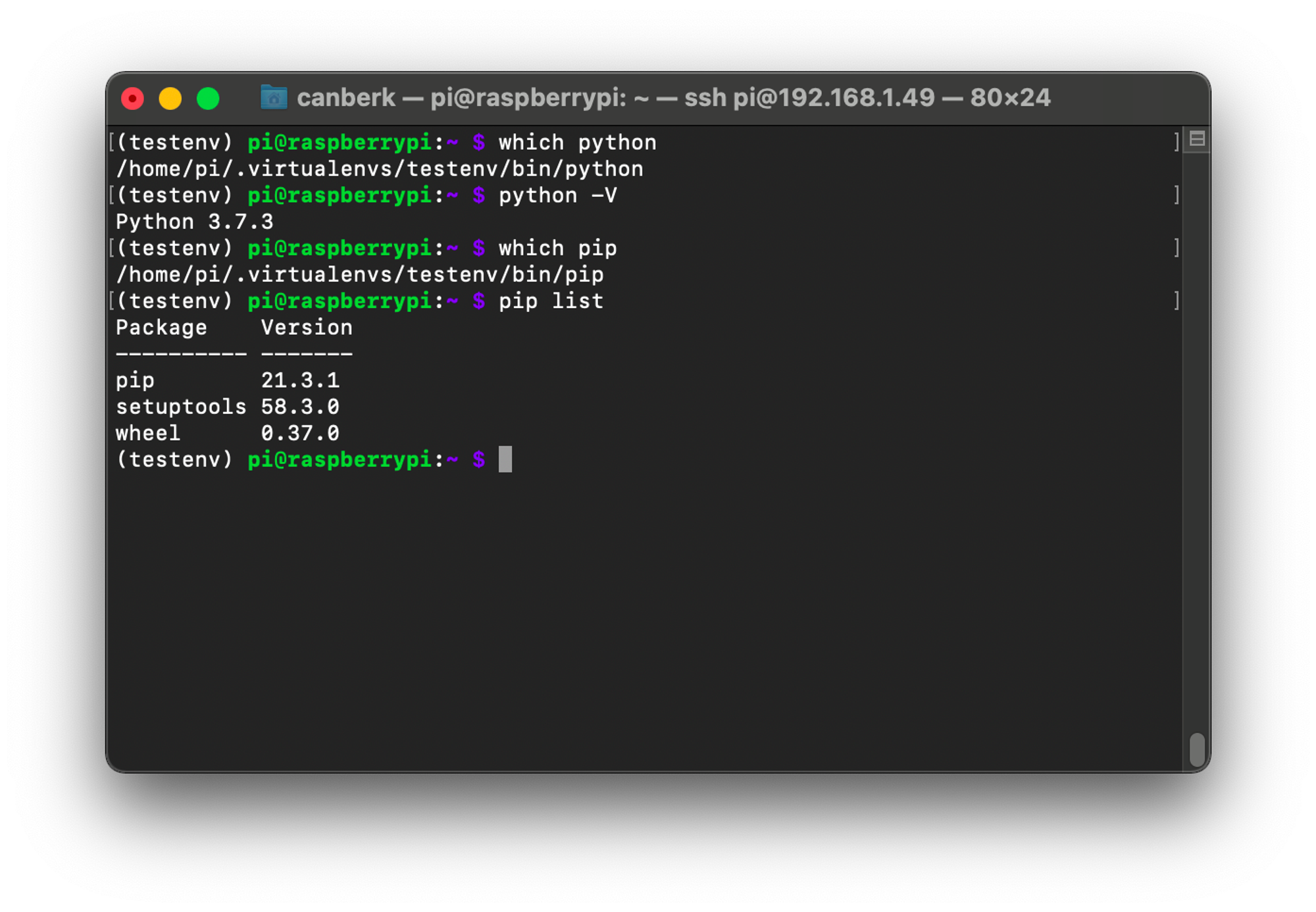
5. Listing and Activating Virtual Environments
We can list the available virtual environments with the workon command.
workonAlso, we can activate the virtual environment of our choice with the workon command with the name of our virtual environment.
workon testenv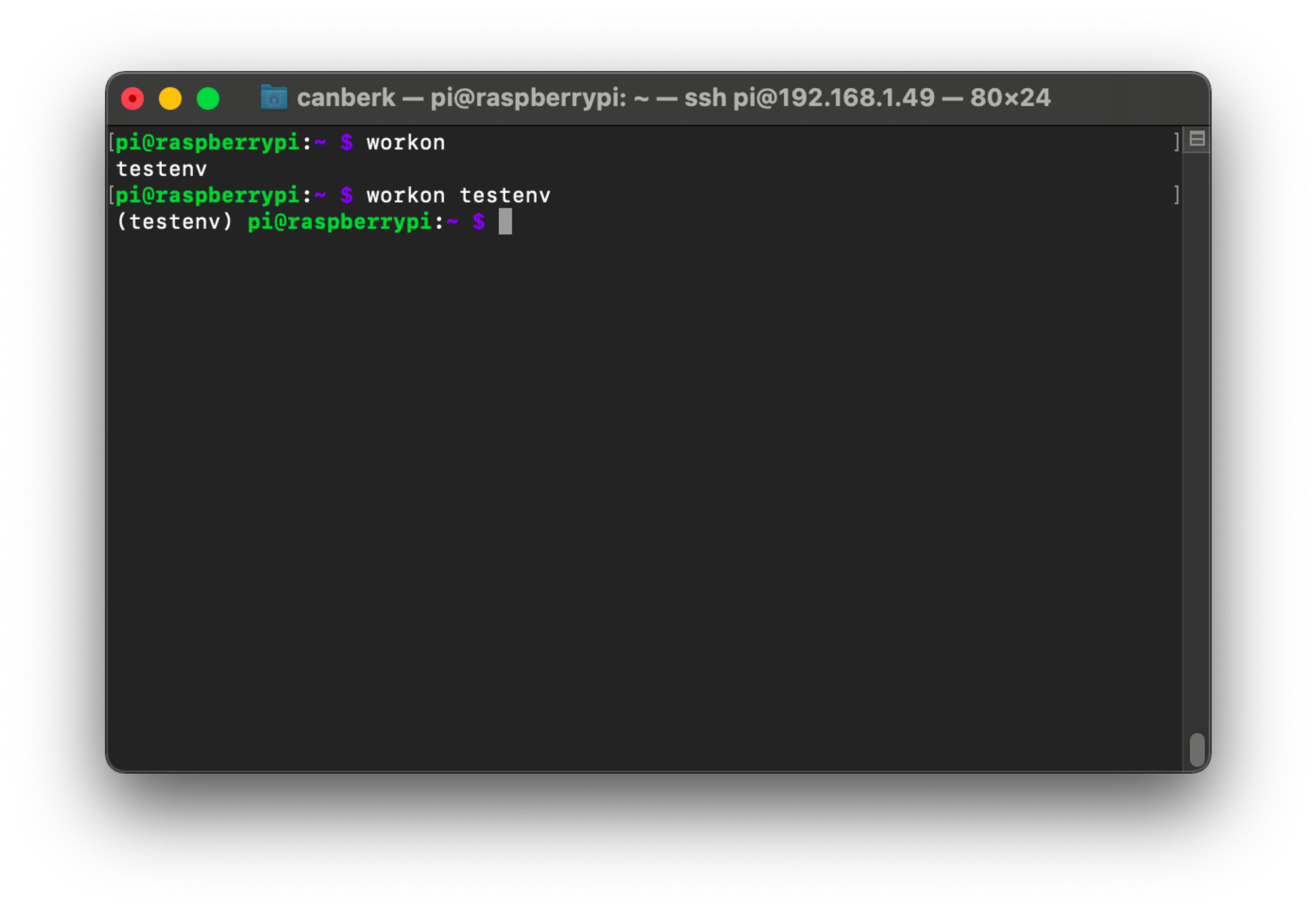
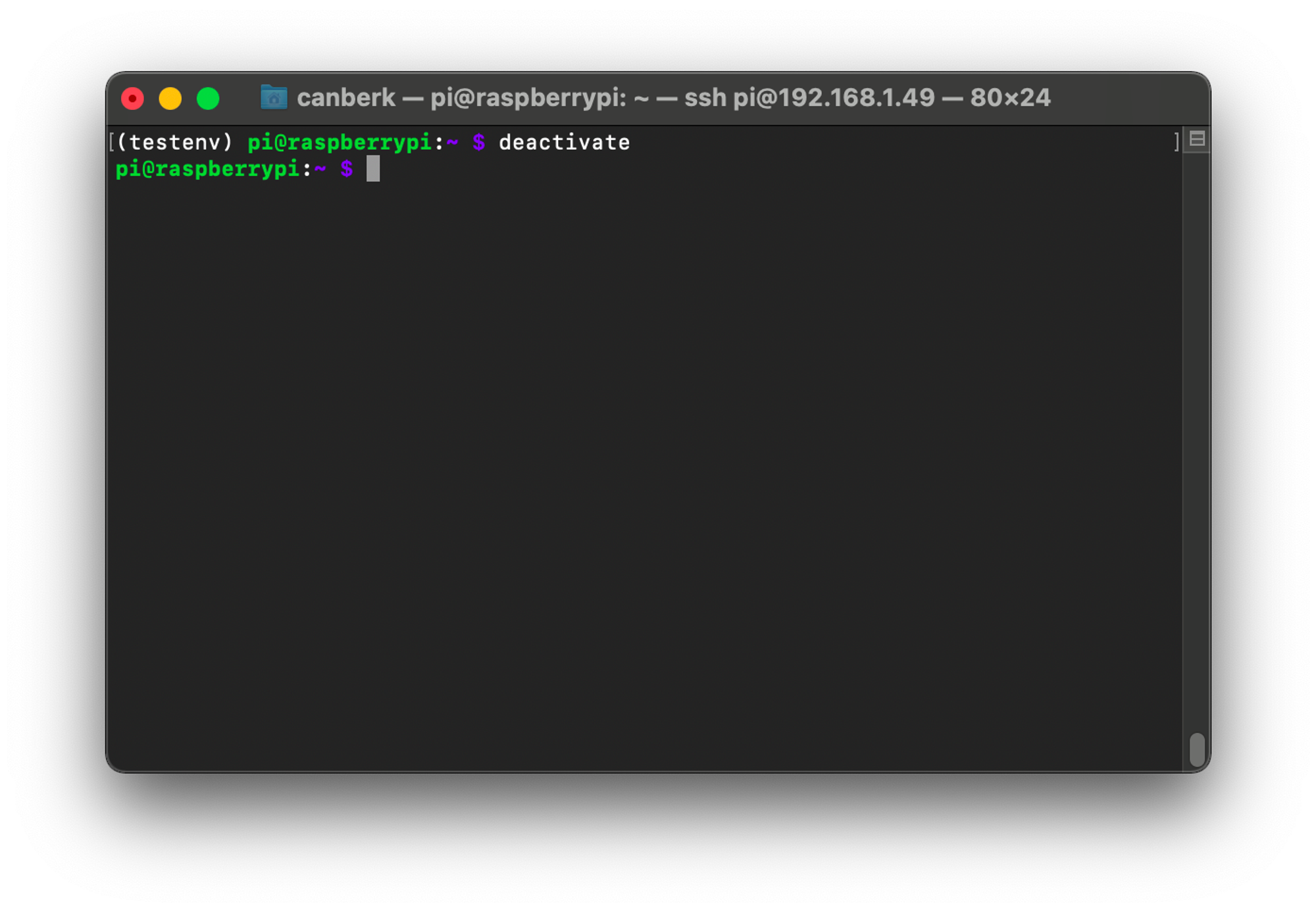
6. Deactivating a Virtual Environment
In order to deactivate a virtual environment, you can use the deactivate command. You can check if a virtual environment is activated or not by checking the beginning of your terminal name.
deactivate